Oxygen has 6 valence electrons, making it an important element for various chemical reactions. Valence electrons are crucial for determining an element’s reactivity and bonding capabilities.
Understanding the number of valence electrons in oxygen is essential for predicting its behavior in different compounds and environments. Oxygen’s electron configuration plays a significant role in its role in sustaining life through respiration and its involvement in various chemical processes.
By having 6 valence electrons, oxygen can form stable bonds with other elements, contributing to its versatility and widespread presence in nature.
Credit: socratic.org
The Basics Of Valence Electrons
Oxygen has six valence electrons, located in its outermost energy level. These electrons play a crucial role in forming chemical bonds. Understanding the basics of valence electrons helps in predicting the reactivity and bonding behavior of elements.
Atomic Structure Primer
Before delving into the basics of valence electrons, let’s quickly refresh our understanding of atomic structure. At the core of an atom lies a positively charged nucleus composed of protons and neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are negatively charged particles called electrons. These electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells, with each shell capable of holding a certain number of electrons.
Role Of Valence Electrons In Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding, as they determine an atom’s ability to form bonds with other atoms. These electrons are located in the outermost energy level or shell of an atom. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses determines its reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form.
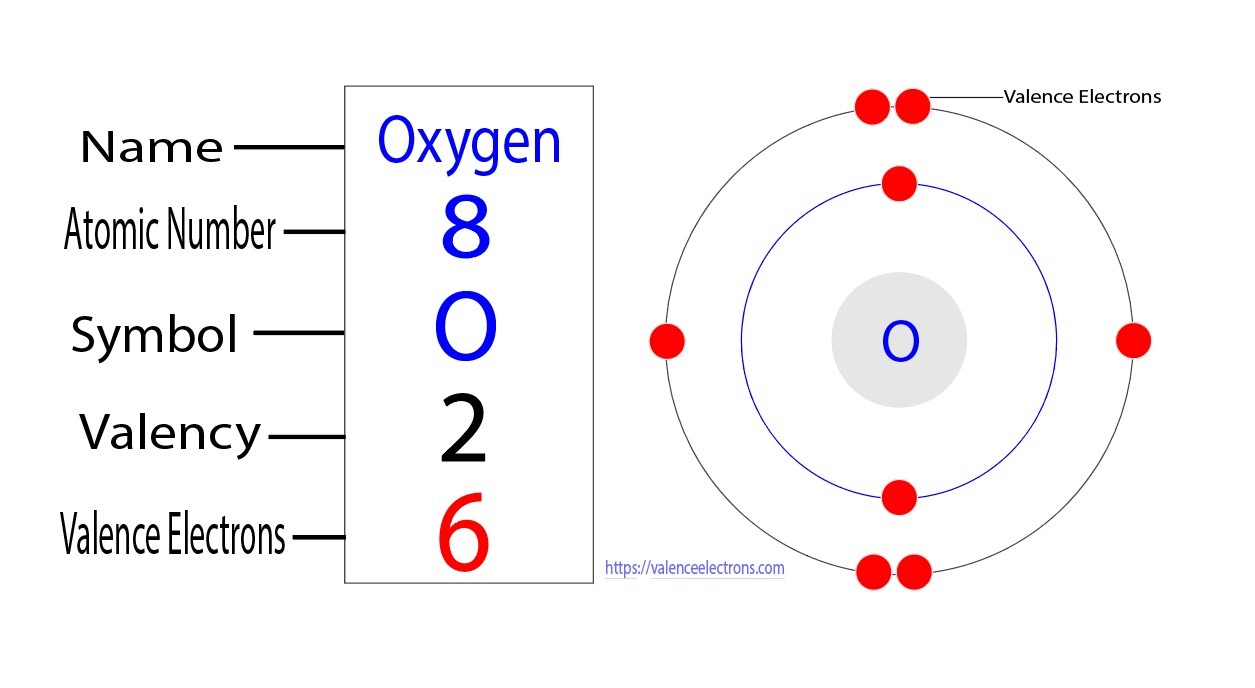
Let’s take the example of oxygen (O), which has an atomic number of 8. Oxygen has two electrons in its inner shell and six electrons in its outermost shell. Therefore, oxygen has six valence electrons. These valence electrons are the ones involved in chemical reactions and bonding with other elements.
Understanding the number of valence electrons an atom has is crucial in predicting its behavior when it comes into contact with other atoms. Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically following the octet rule, which states that atoms strive to have eight valence electrons in their outermost shell.
In the case of oxygen, with six valence electrons, it tends to gain two electrons to achieve a stable configuration of eight valence electrons, similar to the noble gas neon. This tendency to gain electrons is why oxygen is considered an electron acceptor in chemical reactions.
By gaining two electrons, oxygen can form a stable ionic bond with elements such as sodium, which readily donates one electron. This results in the formation of sodium oxide (Na+ + O2-), a compound where oxygen has achieved its desired electron configuration.
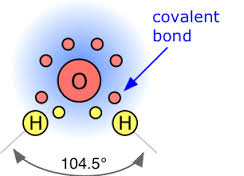
On the other hand, oxygen can also form covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other elements. For example, in the case of water (H2O), oxygen shares two of its valence electrons with two hydrogen atoms, allowing both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
In summary, valence electrons are essential in understanding an atom’s behavior and its ability to form chemical bonds. By knowing the number of valence electrons an atom possesses, we can predict its reactivity and the types of bonds it can form, whether they are ionic or covalent.
Credit: praxilabs.com
Oxygen’s Position In The Periodic Table
How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have? Oxygen is a non-metallic element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen makes up about 21% of the Earth’s atmosphere and is the third-most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium.
Elemental Characteristics
Oxygen has six valence electrons and belongs to the group of elements called chalcogens. It is a highly reactive element and readily forms compounds with most other elements. Oxygen is a pale blue gas at room temperature and is essential for life as it is involved in the process of respiration. It is also used in various industries such as steel production, water treatment, and medical applications.
Group And Period Insights
| Group | Period |
|---|---|
| 16 (Chalcogens) | 2 |
Oxygen is located in group 16, also known as the chalcogens or oxygen family. This group contains elements with similar properties such as high electronegativity and a tendency to form compounds with metals. Oxygen is also located in period 2 of the periodic table, which means it has two energy levels or shells of electrons. The position of oxygen in the periodic table provides insights into its chemical and physical properties as well as its behavior in chemical reactions.
- Oxygen is highly reactive due to its six valence electrons.
- It readily forms compounds with most other elements.
- Oxygen is essential for life and various industrial applications.
- It belongs to the chalcogen group and is located in period 2 of the periodic table.
Determining Valence Electrons
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. Valence electrons determine an element’s reactivity and bonding capabilities. Oxygen’s 6 valence electrons contribute to its ability to form stable compounds.
Electron Configuration
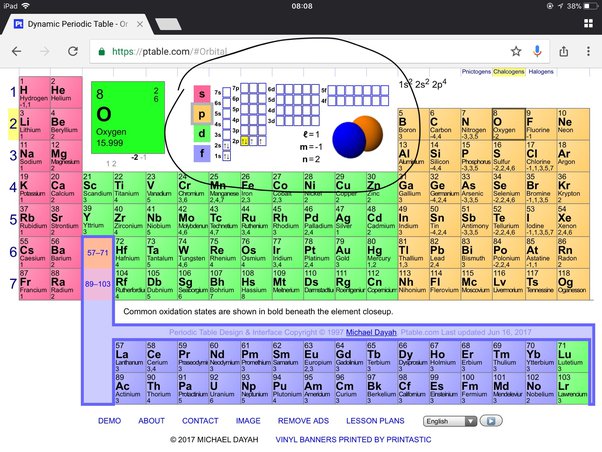
Determining the number of valence electrons in an atom is essential in understanding its chemical behavior and reactivity. One way to determine the valence electrons is by examining the electron configuration of the atom. The electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in different energy levels or orbitals within an atom. The electron configuration of oxygen is 1s224. This notation represents the arrangement of electrons in the atom’s orbitals. The numbers and letters represent the principal energy level (n), the sublevel (s or p), and the number of electrons in that sublevel. In the case of oxygen, the 1s sublevel has 2 electrons, the 2s sublevel has 2 electrons, and the 2p sublevel has 4 electrons.
Valence Shell Examination
Another method to determine the number of valence electrons is by examining the atom’s valence shell. The valence shell is the outermost energy level of an atom. For oxygen, the valence shell is the second energy level (n=2), which consists of the 2s and 2p orbitals. To find the number of valence electrons in oxygen, we look at the highest energy level, which is the valence shell. In this case, the valence shell contains 6 electrons, as there are 2 electrons in the 2s orbital and 4 electrons in the 2p orbitals.
Therefore, oxygen has 6 valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons in an atom is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and interactions with other atoms. The valence electrons are the ones involved in bonding and determining the atom’s oxidation state. In the case of oxygen, its 6 valence electrons contribute to its ability to form covalent bonds and participate in various chemical reactions. In conclusion, the number of valence electrons in oxygen can be determined through the examination of its electron configuration or by identifying the electrons in its valence shell. With 6 valence electrons, oxygen exhibits specific chemical properties that make it an essential element in various compounds and biological processes.
Oxygen’s Valence Electrons
Oxygen, a crucial element in the periodic table, possesses six valence electrons. These electrons are located in the outermost shell of an oxygen atom and play a significant role in its chemical behavior. Understanding the concept of valence electrons is essential in comprehending the reactivity and bonding tendencies of oxygen and its compounds.
Quantifying Oxygen’s Valence
Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, is situated in group 16 of the periodic table, indicating that it has six valence electrons. These electrons are crucial in forming chemical bonds with other elements, influencing the overall stability and reactivity of oxygen-containing compounds.
Implications For Reactivity
The presence of six valence electrons in an oxygen atom gives rise to its tendency to form covalent bonds with other elements, resulting in the creation of various compounds. This reactivity also enables oxygen to participate in essential biological processes and the formation of diverse materials in the natural environment.
Visualizing Oxygen’s Electron Configuration
Oxygen has six valence electrons, making it highly reactive and likely to form compounds with other elements. Visualizing its electron configuration, with two electrons in the first energy level and six in the second, helps understand its chemical behavior.
Orbital Diagrams
Orbital diagrams are a visual representation of the electron configuration of an atom. They provide a way to easily understand and visualize how the electrons are distributed within the energy levels and orbitals of an atom. When it comes to oxygen, which has the atomic number 8, the orbital diagram helps us to see its electron configuration.
Oxygen has a total of 8 electrons, and these electrons are distributed across the atom’s energy levels and orbitals. In the orbital diagram for oxygen, the first energy level (n=1) can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, and the second energy level (n=2) can hold a maximum of 8 electrons. The electrons are placed in the orbitals following a specific pattern known as the Aufbau principle.
In the case of oxygen, the orbital diagram would show two electrons in the first energy level and six electrons in the second energy level. The first energy level has a single s orbital, which can hold 2 electrons, while the second energy level has both an s and a p orbital. The s orbital can hold 2 electrons, while the p orbital can hold 6 electrons.
Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis dot structures are another way to visualize the electron configuration of an atom. They use the element’s symbol and dots to represent the valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and are involved in chemical bonding.
For oxygen, which is in Group 16 of the periodic table, it has 6 valence electrons. In a Lewis dot structure, these 6 valence electrons would be represented by placing 6 dots around the element’s symbol, with no more than 2 dots per side.
So, when visualizing oxygen’s electron configuration using Lewis dot structures, you would see the element’s symbol “O” with 6 dots surrounding it, representing the 6 valence electrons.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Chemical Behavior Of Oxygen
Oxygen is a highly reactive element with important chemical behaviors that influence its role in compound formation and its oxidation states. Understanding these aspects is crucial for comprehending the fundamental properties of oxygen.
Oxygen In Compound Formation
Oxygen readily forms compounds with various elements, showcasing its versatile nature. Common examples include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and rust (Fe2O3). This propensity for compound formation contributes significantly to the diversity of chemical substances found in nature and human-made materials.
Oxidation States Of Oxygen
Oxygen exhibits different oxidation states in compounds, playing a key role in numerous chemical reactions. It commonly displays an oxidation state of -2 in compounds, such as in water and most metal oxides. However, in certain cases, it can also exhibit oxidation states of -1 (in peroxides) and -1/2 (in superoxides), reflecting its ability to engage in a wide range of chemical interactions.
Comparing Oxygen With Other Elements
Oxygen, an essential element, has 6 valence electrons. Its electron configuration allows it to form bonds with other elements, making it crucial for various chemical reactions and the sustenance of life.
Valence Trends Across The Periodic Table
Oxygen is a key element in the periodic table. It has 6 valence electrons. When we compare oxygen with other elements, we can observe interesting trends.
Oxygen Vs. Other Chalcogens
In the chalcogen group, which includes oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, oxygen has the second-highest electronegativity. This means that oxygen has a strong attraction for electrons.
| Element | Number of Valence Electrons |
|---|---|
| Oxygen (O) | 6 |
| Sulfur (S) | 6 |
| Selenium (Se) | 6 |
| Tellurium (Te) | 6 |
Applications And Significance
Oxygen plays a crucial role in various applications and industries due to its unique properties.
Oxygen In Organic Chemistry
Oxygen’s high electronegativity influences chemical reactions in organic compounds.
Industrial And Environmental Relevance
Oxygen is vital in industrial processes like steel production and environmental applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Atomic Number Of Oxygen?
The atomic number of oxygen is 8, indicating the number of protons in its nucleus. This characteristic defines its chemical behavior and its position in the periodic table.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have?
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons, contributing to its ability to form various chemical bonds, making it essential for life and many industrial processes.
What Is The Significance Of Oxygen’s Valence Electrons?
Oxygen’s valence electrons enable it to form strong bonds with other elements, crucial for the formation of water, organic compounds, and the transfer of energy in biological systems.
How Does The Number Of Valence Electrons Affect Oxygen’s Reactivity?
Oxygen’s 6 valence electrons make it highly reactive, enabling it to participate in oxidation-reduction reactions, combustion, and the support of life-sustaining processes.
Conclusion
Oxygen is an essential element in our atmosphere, and it has six valence electrons. Understanding the valence electrons of an atom is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and reactivity. Oxygen has two unpaired electrons in its outermost shell, making it highly reactive and capable of forming strong covalent bonds with other elements.
Knowing the number of valence electrons of an atom is essential in understanding its chemical properties, and this knowledge can be applied in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and materials science.