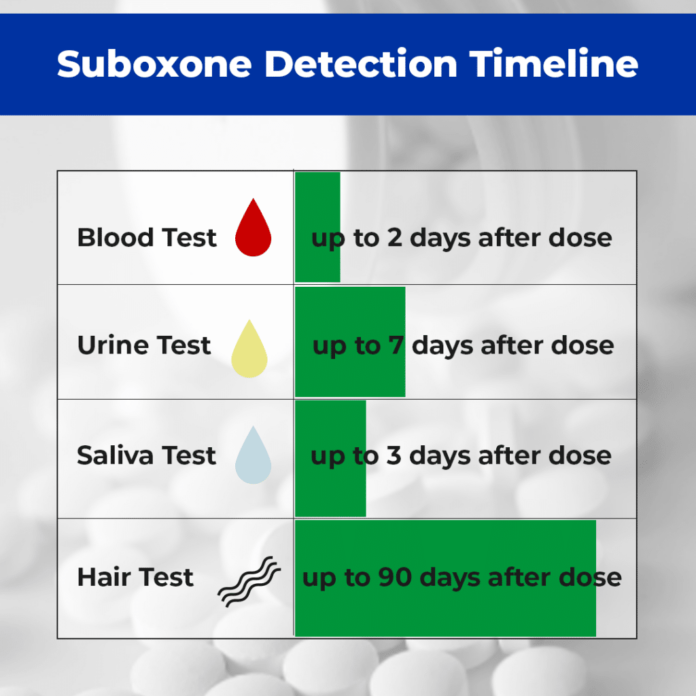
Suboxone can be detected in your system for up to 2-3 days after last use. Suboxone’s elimination half-life is around 24-42 hours.
Factors like metabolism, hydration, dosage, and frequency of use can affect detection times. If you have taken Suboxone, it’s essential to be aware of how long it stays in your system for various reasons. This information is crucial for drug testing, medical procedures, and overall health management.
Understanding the duration Suboxone remains in your system enables you to make informed decisions regarding its usage and potential interactions with other medications or substances. By staying informed about its presence in your body, you can take necessary precautions and seek appropriate medical guidance.
Credit: www.recoverydelivered.com
Introduction To Suboxone
Suboxone typically stays in your system for about 2-3 days, varying based on metabolism and usage. Its half-life is approximately 24-60 hours, affecting the duration it remains detectable. Various factors influence this timeframe, including frequency of use and individual differences.
Suboxone is a medication that is commonly used in the treatment of opioid addiction. It is a combination of two active ingredients: buprenorphine and naloxone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, which means it activates the same receptors in the brain as opioids but with less intensity. Naloxone, on the other hand, is an opioid antagonist that blocks the effects of opioids. Together, these two components help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, making it easier for individuals to overcome opioid addiction.
What Is Suboxone?
Suboxone is a prescription medication that is primarily used in medication-assisted treatment (MAT) programs for opioid addiction. It is available in the form of sublingual tablets or films, which are dissolved under the tongue. The combination of buprenorphine and naloxone in Suboxone makes it an effective tool in managing opioid dependence. Buprenorphine helps alleviate withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, while naloxone helps prevent misuse or abuse of the medication.
Purpose Of Suboxone In Detox
The main purpose of Suboxone in detoxification is to help individuals safely and comfortably withdraw from opioids. When someone stops using opioids abruptly, they often experience intense withdrawal symptoms, which can be extremely challenging to endure. Suboxone is used to alleviate these symptoms and provide relief during the detoxification process. It helps stabilize the individual by reducing cravings and minimizing the physical and psychological distress associated with opioid withdrawal.
During detox, Suboxone is typically administered under the supervision of a healthcare professional. The dosage and duration of treatment may vary depending on the individual’s needs and the severity of their addiction. The ultimate goal is to gradually taper off the medication while providing support and counseling to address the underlying issues contributing to addiction.
In conclusion, Suboxone is a valuable medication in the treatment of opioid addiction. It helps individuals manage withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and transition towards a drug-free lifestyle. However, it is important to note that Suboxone should always be used as part of a comprehensive treatment program that includes counseling, therapy, and ongoing support to maximize its effectiveness.
Suboxone’s Active Ingredients
Suboxone contains two main active ingredients, buprenorphine and naloxone, which work together to manage opioid dependence. The duration Suboxone stays in your system varies but typically can be detected in urine for 7-10 days after the last dose.
Suboxone’s Active Ingredients: Suboxone is a medication used to treat opioid addiction. It is a combination of two active ingredients: buprenorphine and naloxone. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, meaning it binds to the same receptors in the brain as opioids but produces a weaker effect. Naloxone is an opioid antagonist, which means it blocks the effects of opioids.
Buprenorphine’s Role
Buprenorphine is the main active ingredient in Suboxone and is responsible for reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms in people addicted to opioids. Buprenorphine has a long half-life, which means it stays in the system for a long time. It can take up to 10 days for buprenorphine to be completely eliminated from the body.
Naloxone Explained
Naloxone is added to Suboxone to prevent misuse. Naloxone has a high affinity for opioid receptors, which means it can displace other opioids from the receptors and reverse their effects. Naloxone is not absorbed well when taken orally, but it is effective when injected or taken intranasally. Naloxone has a short half-life, which means it is eliminated from the body relatively quickly.
In summary, Suboxone’s active ingredients work together to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in people addicted to opioids. Buprenorphine has a long half-life and stays in the system for up to 10 days, while naloxone has a short half-life and is eliminated from the body relatively quickly. This combination makes Suboxone an effective treatment for opioid addiction.
Duration Of Action
How Long Does Suboxone Stay in Your System? Suboxone typically stays in the system for 2-3 days. However, the duration can vary based on metabolism and individual factors. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized information.
Half-life Of Suboxone
Understanding the duration of action of Suboxone can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan. One crucial aspect to consider is the half-life of Suboxone. The half-life refers to the time it takes for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. In the case of Suboxone, the half-life can vary depending on several factors.
On average, the half-life of Suboxone is approximately 24-60 hours. However, it’s important to note that this is just an estimate, as individual variations can occur. Factors such as age, metabolism, liver function, and dosage can influence how long Suboxone stays in the body.
Factors Affecting Duration
Several factors can affect the duration of action of Suboxone:
- Metabolism: Individuals with a faster metabolism tend to eliminate Suboxone from their system more quickly. Conversely, those with a slower metabolism may experience a longer duration of action.
- Dosage: The amount of Suboxone taken can impact how long it stays in the body. Higher doses may take longer to be eliminated compared to lower doses.
- Liver Function: The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing Suboxone. If liver function is impaired, it may take longer for the drug to be processed and eliminated.
- Body Mass: Individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) may have a longer duration of action for Suboxone as the drug can accumulate in fatty tissues.
- Frequency of Use: Regular use of Suboxone can lead to its accumulation in the body, resulting in a longer duration of action.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine how long Suboxone may stay in your system based on your specific circumstances. They can provide personalized guidance and support throughout your treatment journey.
Credit: www.bicyclehealth.com
Effects On The Body
Suboxone can stay in the body for around 2-3 days after the last dose. It is broken down in the liver and eliminated through urine. Factors like metabolism and dosage can affect how long it stays in the system. Regular use can lead to accumulation in the body over time.
Immediate Effects
Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid addiction, has immediate effects on the body upon ingestion. When taken as prescribed, it works by binding to the same receptors in the brain that opioids target, thereby reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. The active ingredients in Suboxone, buprenorphine, and naloxone, start to take effect within 30 minutes to an hour after administration.
Long-term Use Considerations
Long-term use of Suboxone can have various effects on the body. It is important to note that Suboxone is a long-acting medication, which means it stays in the system for an extended period compared to other opioids. The half-life of Suboxone is around 24-60 hours, meaning it takes that amount of time for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. During long-term use, Suboxone can have both positive and negative effects on the body. Some positive effects include reducing the risk of overdose and improving overall quality of life by allowing individuals to focus on recovery.
However, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects such as constipation, nausea, dizziness, and sleep disturbances. It is worth mentioning that the duration Suboxone stays in the body can vary depending on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, individual metabolism, and liver function.
Additionally, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns or adjustments to the treatment plan. In conclusion, Suboxone has immediate effects on the body, helping to alleviate cravings and withdrawal symptoms. However, long-term use should be carefully monitored, considering both the positive effects and potential side effects. Understanding the duration of Suboxone in the system can aid in optimizing the treatment plan and ensuring a successful recovery journey.
The Detox Process
The detox process of Suboxone involves several stages and requires careful management of withdrawal symptoms. Understanding the timeline of detox and the strategies for handling withdrawal can help individuals prepare for this critical phase of recovery.
Stages Of Detox
The detox process for Suboxone typically occurs in several stages, each with its own timeline and challenges. These stages include:
- Initiation of detox
- Peak withdrawal symptoms
- Resolution of acute withdrawal
- Management of post-acute withdrawal symptoms
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
During the detox process, managing withdrawal symptoms is crucial for the individual’s comfort and safety. This involves:
- Medication-assisted treatment
- Monitoring by healthcare professionals
- Supportive care and counseling
- Addressing co-occurring mental health conditions

Credit: www.avenuesrecovery.com
Treatment Protocols
Treatment protocols for Suboxone are essential to understand for both patients and healthcare providers. These protocols cover important aspects such as recommended dosages and the process of tapering off Suboxone.
Recommended Dosages
The recommended dosages for Suboxone are determined based on the individual’s opioid dependence and response to treatment. Typically, the initial dosage is 4mg/1mg to 24mg/6mg sublingually once daily. It is crucial for patients to adhere to the prescribed dosage and not adjust it without consulting their healthcare provider.
Tapering Off Suboxone
Tapering off Suboxone involves gradually reducing the dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Healthcare providers create personalized tapering plans based on the patient’s progress and overall health. This process requires close monitoring to ensure a smooth transition and reduce the risk of relapse.
Potential Side Effects
When taking Suboxone, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects that may arise. Understanding these effects can help you manage your medication better.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Headache
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Constipation
Addressing Adverse Reactions
If you experience severe allergic reactions such as rash, itching, swelling, or trouble breathing, seek immediate medical attention.
Recovery And Support
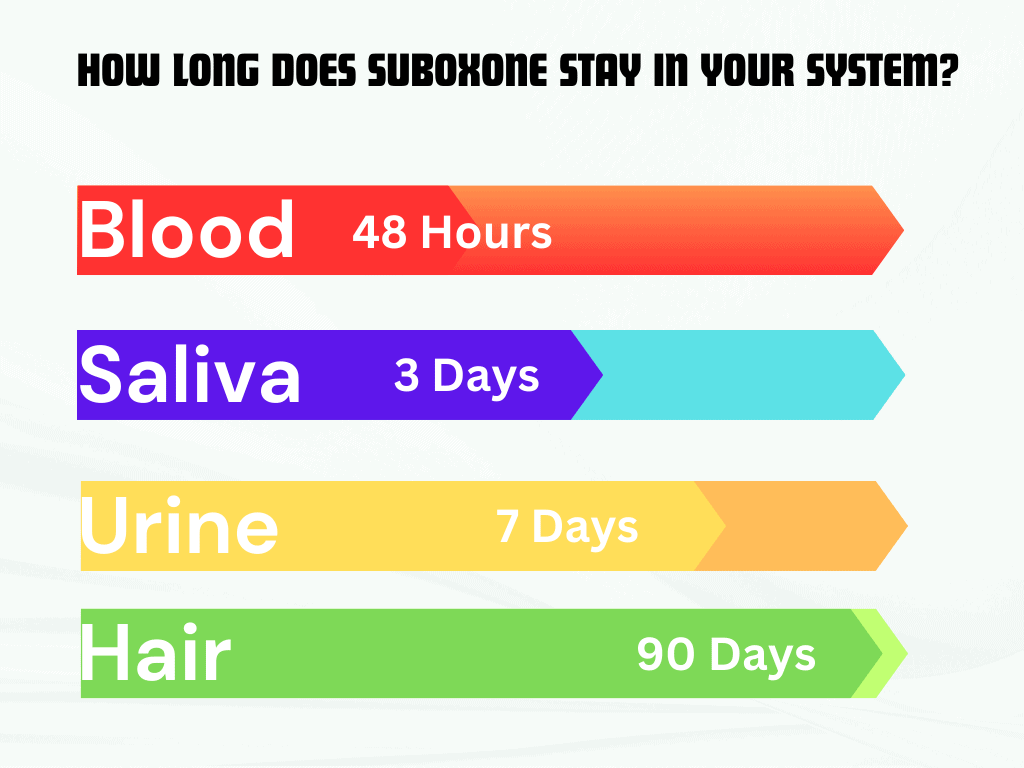
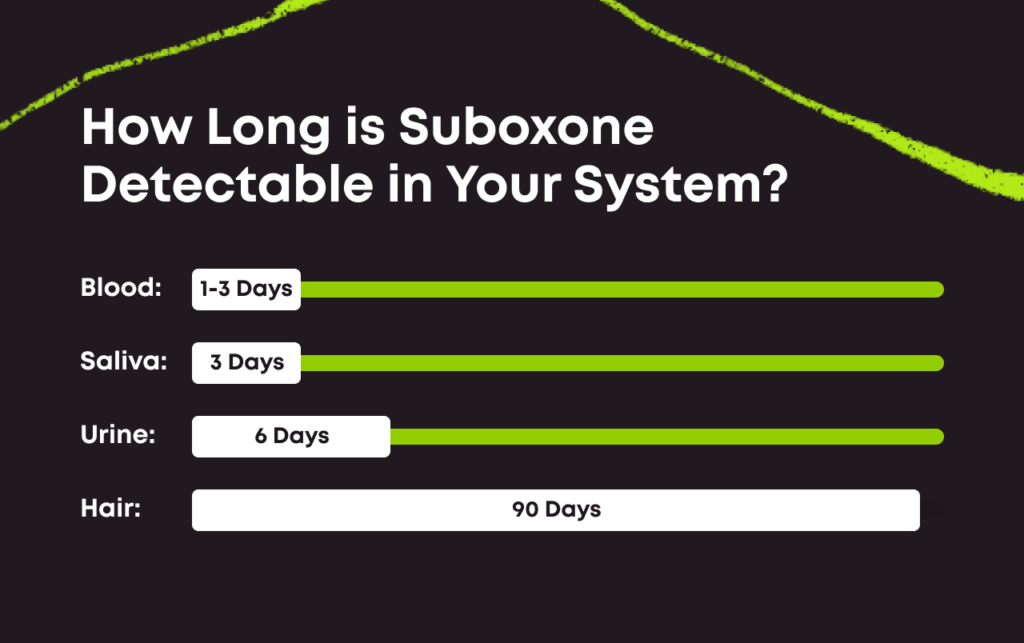
Suboxone, a medication used for opioid addiction treatment, can stay in your system for varying lengths of time. Factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism can affect the duration. On average, it can be detected in urine for up to 3-4 days, in saliva for 1-2 days, and in blood for about 24 hours.
Aftercare Programs
After completing Suboxone treatment, aftercare programs play a vital role.
Structured support helps individuals transition back to daily life smoothly.
Counseling, therapy, and support groups are common aftercare options.
Support Systems And Resources
Building a strong support system is crucial for long-term recovery.
Family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional and practical help.
Online resources and helplines offer accessible support anytime.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Suboxone Stay In Your System?
Suboxone can be detected in urine for up to 2-4 days, in blood for up to 24 hours, and in saliva for up to 1-10 days, depending on various factors such as metabolism and dosage.
What Factors Affect Suboxone’s Duration In The Body?
The duration of Suboxone in the body can be influenced by metabolism, dosage, frequency of use, hydration level, and individual body characteristics.
Can Suboxone Show Up In A Drug Test?
Yes, Suboxone can be detected in drug tests. It is advisable to inform the testing facility about any prescribed medications, including Suboxone, to avoid misinterpretation of results.
How Does Metabolism Affect Suboxone Clearance?
Metabolism plays a significant role in clearing Suboxone from the body. Factors such as liver function and overall metabolic rate can impact the duration of Suboxone in the system.
Conclusion
Suboxone is a powerful drug that can remain in your system for a considerable period of time, depending on various factors such as your metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use. Understanding how long Suboxone can stay in your system is essential for those who are undergoing treatment for opioid addiction.
While there is no definitive answer, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and seek professional help if you are struggling with addiction. Remember that recovery is possible with the right support and determination.