Mosquitoes typically live for about 2 weeks. Factors like species, environment, and climate can affect their lifespan.
Mosquitoes are pesky insects that can cause discomfort and transmit diseases. Understanding their life cycle and lifespan is essential in controlling their population. By learning how long mosquitoes live, we can take proactive measures to reduce their numbers and protect ourselves from their bites.
Let’s delve deeper into the intriguing world of mosquitoes and explore the factors that influence their lifespan. From breeding habits to environmental conditions, various elements play a role in determining how long these buzzing pests stick around. By gaining insights into their lifespan, we can better equip ourselves to combat these tiny yet formidable adversaries.

Credit: www.cleggs.com
Introduction To Mosquito Lifespan
Mosquitoes have a relatively short lifespan, typically living for about two weeks to a month. However, the exact duration varies based on factors such as species, environmental conditions, and gender. Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial in developing effective strategies for controlling their populations.
Mosquitoes are known for their itchy bites and their ability to spread deadly diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial to controlling their population and preventing the spread of diseases. In this section, we will explore the factors that influence mosquito lifespan and the importance of understanding their life cycle.
Factors Influencing Lifespan
The lifespan of mosquitoes varies depending on the species, gender, and environmental conditions. Female mosquitoes typically live longer than males as they require more time to lay eggs. The average lifespan of a mosquito ranges from a few days to several months. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and availability of food also play a significant role in the lifespan of mosquitoes. Mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid conditions and require water to breed. They feed on nectar and plant juices, but female mosquitoes require blood to lay eggs.
Importance Of Understanding Mosquito Life Cycle
Understanding the life cycle of mosquitoes is essential for effective mosquito control. Mosquitoes go through four stages in their life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage requires different environmental conditions and offers unique opportunities for control. Eliminating standing water, where mosquitoes lay their eggs, can help reduce their population. Treating stagnant water with larvicides can also prevent the larvae from developing into adults. Mosquito nets, insecticides, and repellents can be used to protect against adult mosquitoes.
In conclusion, understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial for preventing the spread of deadly diseases and controlling their population. By addressing the factors that influence their lifespan and targeting different stages of their life cycle, we can effectively reduce their impact on human health.
Mosquito Birth And Early Development
How Long Do Mosquitoes Live? Mosquitoes have a relatively short lifespan, with most species living around 2-3 weeks. However, the exact length can vary depending on factors such as temperature and availability of food sources. During this time, mosquitoes go through a complex life cycle that includes egg laying, hatching, and larval development before they emerge as adults.
Understanding their life cycle is crucial for effective mosquito control strategies.
Egg Laying And Hatching
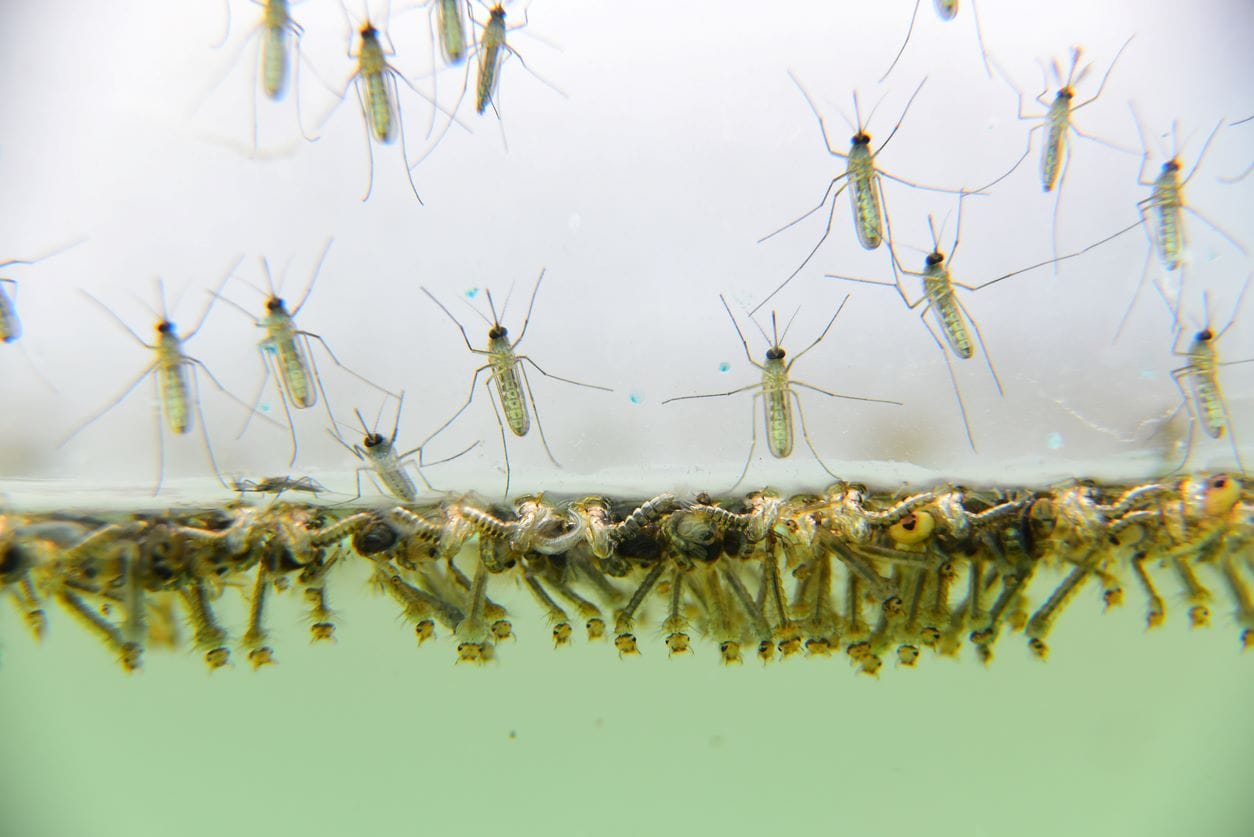
Female mosquitoes lay their eggs in standing water, which can be anything from puddles and ponds to bird baths and flower vases. The eggs are usually laid in clusters, which float on the surface of the water. Depending on the species, mosquitoes can lay anywhere from 100 to 300 eggs at a time. The eggs hatch into larvae within 24 to 48 hours. The larvae then go through four molts over the course of several days, during which they feed on microorganisms and organic matter in the water.
Larval And Pupal Stages
As the larvae grow, they shed their skin and enter the pupal stage, which lasts for about 24 to 48 hours. During this time, the mosquito is transformed from a larva into an adult. Once the pupal stage is complete, the adult mosquito emerges from the water. The length of time it takes for the mosquito to mature from egg to adult varies depending on the species, temperature, and other environmental factors.
In general, mosquitoes can go from egg to adult in as little as 4 days or as long as several weeks. It is important to note that not all mosquitoes are harmful, but some can carry serious diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. Understanding the life cycle of mosquitoes can help us take steps to prevent them from breeding and spreading disease.
Adult Mosquito: Emergence And Maturation
Adult mosquitoes typically live for about 1-2 weeks, with the males having a shorter lifespan than the females. After emerging from the pupal stage, they require a few days to mature and become capable of reproduction. The duration of a mosquito’s life largely depends on environmental factors and species-specific characteristics.
Transition To Adulthood
Mosquitoes, those pesky creatures that buzz around and leave itchy bites, go through a fascinating transformation from egg to adult. The transition from larva to adult mosquito is a crucial stage in their life cycle. Let’s take a closer look at how these tiny insects emerge and mature into adulthood.
Mating Behaviors And Rituals
Once mosquitoes reach adulthood, their primary focus shifts to reproduction. Mating behaviors and rituals play a crucial role in ensuring the continuation of their species. Male mosquitoes are the ones that actively seek out females for mating. They utilize various sensory cues, such as the female’s scent and sound vibrations, to locate a potential partner.
Once a suitable female is found, the mating rituals begin. During the mating process, the male mosquito uses specialized structures called claspers to grasp onto the female’s abdomen. The male then transfers sperm to the female, who stores it for future use. Interestingly, some mosquito species engage in unique mating behaviors, such as forming large swarms or engaging in elaborate courtship dances.
Average Lifespan Of Mosquitoes
Understanding the average lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial for effective pest control and disease prevention. By delving into the factors that influence their longevity, we can develop better strategies for managing these pesky insects. Let’s explore the average lifespan of mosquitoes in more detail.
Male Vs Female Longevity
Female mosquitoes typically have a longer lifespan than males, often living for several weeks. This is due to the fact that males primarily feed on nectar, while females require a blood meal to produce eggs. The process of laying eggs enables females to survive for a more extended period, contributing to their overall longevity.
Species-specific Lifespan Variations
When examining the lifespan of mosquitoes, it’s essential to consider species-specific variations. Different mosquito species exhibit varying lifespans, with some living for only a few days, while others can survive for several weeks or even months. Factors such as environmental conditions, availability of suitable breeding sites, and access to food sources play a significant role in determining the lifespan of different mosquito species.
Environmental Impact On Mosquito Longevity
Mosquitoes, those pesky bloodsuckers, have a relatively short lifespan compared to other insects. However, various environmental factors can significantly affect their longevity. Understanding these factors is crucial in developing effective strategies for mosquito control. In this section, we will explore the environmental impacts on mosquito longevity, focusing on temperature and humidity effects, as well as predation and survival strategies.
Temperature And Humidity Effects
The lifespan of mosquitoes is greatly influenced by temperature and humidity levels in their surroundings. Warmer temperatures accelerate their development and shorten their life cycle, while cooler temperatures slow it down. Mosquitoes thrive in humid environments as it aids in their reproduction, but excessive moisture can also lead to the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
Extreme temperature conditions can be detrimental to mosquito survival. Freezing temperatures during winter can cause adult mosquitoes to die off, while extreme heat can dehydrate and kill them. Mosquitoes are more active during warmer months, where their lifespan can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Predation And Survival Strategies
Mosquitoes face numerous predators in their habitats, and the presence of these natural enemies can significantly impact their longevity. Predators such as birds, bats, dragonflies, and certain fish species feed on mosquitoes and help control their population. These predators play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance and reducing the number of disease-spreading mosquitoes.
In response to predation pressure, mosquitoes have evolved several survival strategies. They lay their eggs in stagnant water bodies, which serve as breeding grounds, to protect them from potential predators. Some mosquito species even have the ability to detect and avoid environments with high predator densities. These adaptations allow mosquitoes to increase their chances of survival and continue their life cycle.
In conclusion, understanding the environmental factors that affect mosquito longevity is essential for effective mosquito control. Temperature and humidity levels play a significant role in their development and lifespan. Predation by natural enemies also influences mosquito populations. By considering these factors, we can develop targeted strategies to manage mosquito populations and minimize their impact on human health.
Mosquitoes’ Role In Ecosystems
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, contributing to the balance and functioning of natural habitats. Despite their reputation as nuisance pests, mosquitoes serve as an essential component of the food web and contribute to the pollination of certain plant species.
Pollination And Biodiversity
Mosquitoes, particularly the males, are involved in pollination by feeding on the nectar of flowers. As they move from flower to flower in search of nectar, they inadvertently transfer pollen, aiding in the reproductive processes of various plant species. This interaction supports biodiversity and contributes to the health of ecosystems.
Mosquitoes As Prey For Other Species
Mosquitoes are an important food source for various organisms, including fish, birds, and insects. By serving as prey, mosquitoes contribute to the energy flow within food chains and webs, supporting the survival and population dynamics of numerous species. Their role as prey helps maintain ecological balance and sustains the diverse array of life within ecosystems.
Disease Transmission And Lifespan
Mosquitoes have a relatively short lifespan, usually ranging from a few weeks to a few months. However, during their short lives, they can transmit various diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus to humans and animals. Preventing mosquito bites and controlling their population are crucial in reducing disease transmission.
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in disease transmission due to their lifespan and ability to carry pathogens.
Mosquito-borne Illnesses
Mosquitoes transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, and Zika virus.
Impact Of Disease On Mosquito Population
Disease can affect mosquito lifespan and population dynamics. Mosquito Lifespan: – Species: Varies from 2 weeks to 6 months. – Female Lifespan: Longer due to blood meals for egg production. Mosquitoes and Disease Transmission: – Vector: Transmit pathogens through bites. – Pathogens: Malaria, Zika, Dengue, West Nile virus. – Prevention: Control breeding sites to reduce disease spread. Disease Impact on Lifespan and Population: – Shortened Lifespan:
Some diseases reduce mosquito lifespan. – Population Control: Disease outbreaks can impact mosquito numbers. Human Role in Disease Control: – Preventive Measures: Use repellents, remove standing water. – Community Efforts: Public health programs for disease prevention. In summary, understanding the relationship between disease transmission and mosquito lifespan is crucial for effective control strategies.
Controlling Mosquito Populations
Controlling mosquito populations is crucial in reducing the spread of diseases and ensuring a comfortable outdoor experience. By implementing effective strategies, it is possible to manage and minimize the presence of these pesky insects.
Preventive Measures
Maintain clean surroundings to eliminate breeding grounds. Dispose of standing water in containers. Use mosquito nets and screens to prevent entry indoors.
Habitat Management
Regularly trim vegetation and grass. Keep gutters clean to avoid water accumulation. Install barriers like fences to limit mosquito access.
Insecticides And Biological Control Methods
Consider using approved insecticides in targeted areas. Explore biological control options like introducing natural predators.
Advancements In Mosquito Research
Mosquitoes have a short lifespan, typically living for around two weeks. However, some species can live for up to a month, while others may only survive for a few days. Advances in mosquito research have allowed scientists to better understand the factors that affect mosquito lifespans, helping to inform mosquito control strategies.
Genetic Studies And Lifespan
Innovations In Mosquito Control
Mosquito research has evolved significantly, with a focus on genetic studies and lifespan. Scientists are exploring ways to manipulate mosquito genetics to reduce their lifespan. This approach shows promise in curbing mosquito populations. Advancements in mosquito control have led to innovative methods. These include the use of biological agents and genetic modification to target mosquito populations effectively. These innovations hold great potential in combating mosquito-borne diseases.

Credit: nadamosquito.com
Conclusion: The Significance Of Mosquito Lifespan
The lifespan of mosquitoes plays a critical role in their ability to transmit diseases. Female mosquitoes can live up to several weeks, while male mosquitoes have a shorter lifespan of only a few days. Understanding the mosquito lifespan is crucial in developing effective strategies for controlling their populations and reducing the spread of mosquito-borne illnesses.
Implications For Human Health
Future Directions In Mosquito Management
Mosquito lifespan directly impacts disease spread and control methods. Understanding mosquito lifespan helps predict disease outbreaks and develop effective control strategies. Mosquito lifespan affects disease transmission rates. Longer lifespan increases disease spread risk. Shorter lifespans can limit disease transmission, aiding in outbreak prevention.
Targeting mosquito lifespan can enhance disease control efforts. Developing strategies to reduce lifespan can help curb disease transmission and protect public health. Research on mosquito lifespan guides future management strategies. By focusing on lifespan modification, we can create targeted interventions for disease prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Mosquitoes Live?
Mosquitoes have a relatively short lifespan, typically ranging from a few weeks to a few months. The exact lifespan depends on various factors, such as species, environmental conditions, and availability of food sources. Female mosquitoes generally live longer than males, with some species surviving up to 8 weeks or more.
Understanding mosquito lifespan is crucial in implementing effective control measures.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial for effective pest control. By learning about their life cycle and longevity, we can implement targeted strategies to minimize their impact. With this knowledge, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from the diseases these insects carry.